
Add to Cart
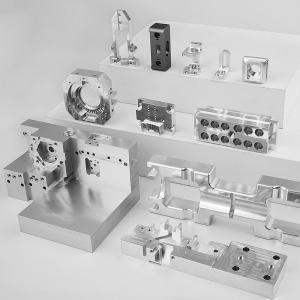
Aluminum Anodized Machining Turned Precision Milled Parts Mini Automatic
Lathe Machine Aluminum Mass CNC Machining Milling Parts
CNC machining, short for computer numerical control machining, is a subtractive manufacturing
technique that utilizes computerized controls and machinery to selectively remove material layers
from a solid block.
Precise cuts in the material are orchestrated through programmed instructions, allowing
automated machinery to execute the machining tasks with accuracy and efficiency.
Product Details
Materials Utilized in CNC Machining
CNC machining is applied to a wide range of materials, each having its unique optimal machining
parameters (speeds and feeds) to ensure effective material removal.
The most frequently used materials include:
Metal
Metal is the most prevalent material in CNC machining. CNC machines
can cut virtually any type
of metal, from easily machinable brass to challenging nickel superalloys like Inconel.
Metal machining spans various applications, including injection molds, shafts, and gears.
Plastic
Although most plastic parts are made through injection molding, CNC
machining is employed for
specific plastic components.
Common materials include ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene), nylon, and polycarbonate.
Plastic machining applications encompass valve bodies, bushings, and prototypes for evaluating
part functionality before investing in costly molding tools.
Wood
CNC routers are frequently used for wood cutting and are generally
more cost-effective than
standard metal-cutting CNC machines.
Wood CNC machining is primarily employed for decorative purposes.
Typical applications encompass furniture, window frames, and ornamental panels.
Foam
Polyurethane foam, whether closed or open-cell, finds extensive use
in CNC machining.
Foam blocks can be shaped into secure packaging for high-value products using a CNC router.
One example is the foam employed in toolboxes to securely hold tools during transport.
Composites
CNC machines are commonly employed in the processing of composite
parts.
Composite materials include a wide range, from aramid to fiberglass to carbon fiber.
These materials are highly abrasive to cutting tools. In aerospace and marine industries,
composite components are machined to add fastener holes and for general trimming post-molding.
| Common Materials | |
| Name | Description |
| Aluminum | High machinability and ductility, good strength-to-weight ratio. |
| Stainless steel | High tensile strength, corrosion and temperature resistant. |
| Mild steel | High machinability and weldability, high stiffness. |
| Brass | Low friction, excellent electrical conductivity, golden appearance. |
| Copper | Excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. |
| Titanium | Excellent strength to weight ratio, used in aerospace, automotive and medical industries. |
| ABS | Common thermoplastic, impact resistant, easy to machine. |
| Nylon | Excellent mechanical properties, thermal, chemical and abrasion resistant. |
| POM | High stiffness, high accuracy, low friction, easy to machine. |
Post-processing and surface finishes for CNC machining
CNC-machined parts as they emerge from the machine often exhibit visible tool marks,
a feature that may not align with your specific part requirements.
Fortunately, there exists a multitude of post-processing techniques aimed at enhancing the
surface appearance and elevating attributes such as wear resistance, corrosion resistance,
and chemical resistance.
Methods like anodizing, bead blasting, and powder coating present viable options for refining
the final presentation of your custom parts, allowing you to achieve the desired surface
quality and performance characteristics.
| Surface Finishes | ||
| Name | Applicable to | Machining marks |
| As machined | Metals, Plastics | Visible, light surface scratches |
| Smooth machining | ||
| Fine machining | Metals | Slightly visible |
| Polishing | Metals | Removed on primary surfaces |
| Bead blasting | Metals | Removed for non-cosmetic, removed on primary surfaces for cosmetic |
| Brushing | Metals | |
| Anodizing Type II | Aluminum | |
| Anodizing Type III | Aluminum | Visible under anodizing |
| Black oxide | Copper, Stainless steel, Alloy steel, Tool steel, Mild steel | Visible |
| Powder coating | Metals | Removed |
| Brushed + electropolishing | Stainless steel | Removed on Primary surfaces |
Specialist Industries
CNC machining finds extensive applications across various industries.
It is prevalent in aerospace, automotive, consumer electronics, robotics, agriculture,
and numerous sectors that heavily rely on metal components.
Furthermore, CNC machining is widely employed in the medical device industry, household
products manufacturing, energy sector, oil and gas industry, and various consumer-oriented
applications.
It stands as one of the most prevalent and versatile manufacturing processes globally.
Company Profile
FAQ's
1. How much does CNC machining cost?
The cost of CNC machining is determined by several key factors, including the complexity of the
part, the quantity of parts needed, and the required lead time.
To obtain an accurate cost estimate, you can upload a 3D CAD model and receive an interactive
quote that includes valuable design for manufacturability (DFM) feedback.
Our CNC machining services do not involve any upfront non-recurring engineering (NRE) costs.
This is made possible through our proprietary software and automated fixturing processes.
As a result, even small quantities of parts, ranging from 1 to 200 units, are cost-effective when
produced using CNC machining.
While CNC machining prices may be comparable to or slightly higher than those of 3D printing,
it offers distinct advantages in terms of superior material properties and surface finishes.
2. A Brief Overview of CNC Machining Parameters
In CNC machining, many parameters are determined by the machine operator during the
generation of G-code.
Among these parameters, we will focus on the build size and accuracy of CNC machines.
CNC machines are known for their relatively large build areas, particularly when compared to
3D printers.
CNC milling systems, for instance, are capable of machining parts with dimensions of up to
2,000 x 800 x 100 mm (78” x 32” x 40”), while CNC turning systems can handle parts with
diameters of up to Ø 500 mm (Ø 20’’).
One of the notable advantages of CNC machining is its ability to produce parts with exceptional
accuracy and tight tolerances.
CNC machines can achieve tolerances that are even less than half the diameter of an average
human hair, which is approximately ± 0.025 mm or .001’’.
In cases where the tolerance is not specified in the technical drawing, the operator typically
machines the part with an accuracy level of 0.125 mm (.005’’).
3. How long does delivery time and quotation take?
Our delivery time and quotation process are influenced by the complexity of your project.
For low-complexity parts, expect a lead time of 2-3 days.
As complexity increases, the lead time can range from 2-5 days.
High-complexity parts may require a lead time of 5-15 days.
Quotation turnaround time varies based on complexity as well.
For straightforward designs, we can provide a quote within 1 business day or even faster.
However, for more intricate projects, the quoting process may take 3 or more business days.
If you have a design that needs assessment and a quote from our team, please don't hesitate
to contact us.
